AI-Powered Asset Management: From Experimentation…

Discover how autonomous trains are transforming public transport in France and Europe. This study explores technical features, costs, and organizational impacts, offering insights and best practices for all key mobility stakeholders.

The global public transport sector is undergoing significant transformations, driven by growing trends and regulations for sustainable, efficient, and user-friendly mobility solutions. Key driver trends include stricter environmental regulations, the push for sustainability, rapid urbanization as well as the growing adoption of Mobility-as-a-Service and digital transformation.
Our study focuses on:
> Geographical scope: France and Europe
> Functional scope: passenger transport
> Technical scope: technologies used, infrastructures…
> Stakeholder scope: the study investigates how autonomous trains can enhance mobility for key actors that are Public Transport Authorities, Public Transport Operators, Infrastructure Manager and Manufacturers.
Grades of Automation (GoA) in train operations levels are defined by the International Association of Public Transport (UITP). There are four main GoA levels:
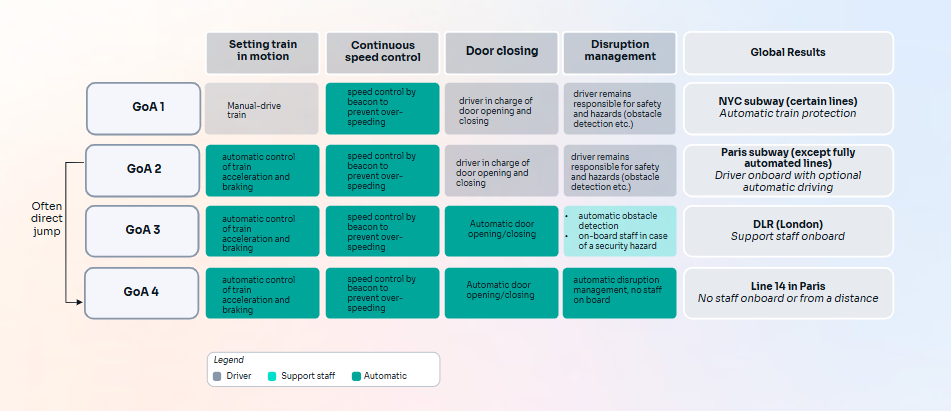
There are two main approaches to switching to autonomous train operations:
Costs vary depending on the GoA level. Trackside and on-board costs increase form GoA2 and GoA4 as the increased level of automation requires more components. Additionally, OPEX and telecommunications costs also increase with higher level of automation.
Switching to autonomous train operations has impacts not only from a technical point of view but also from an organizational point of view. In fact, both on-board and off-board railway professions are impacted such as:
The extent of these impacts depends on the GoA level. Responsibilities can either be reduced, reassigned or transformed. For example, at high GoA levels, drivers are no longer required to be onboard. Switching to autonomous train operations requires planning, training and change management to ensure a smooth transition.
We have identified the key best practices, challenges, and opportunities for each type of stakeholder. We have also developed strong convictions tailored to the specificities of each actor.
Managing Director | Paris
In 2018, Maria started steering the firm’s Mobility working group with the goal of developing offers and expertise through French offices. Since 2021, she is in charge of Sia Partners’ Mobility & Logistics global team and leads the firm’s research and development as well as business development.
